Safe Computing: Understanding PII, Cookies, and Encryption
Big Idea 5: Safe Computing
Safe computing revolves around Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and how it is exploited or kept secure.
What is PII (Personally Identifiable Information)?
PII includes any information that identifies a user on the internet, such as:
- Social Security Number
- Full Name
- Driver’s License
Cookies
Cookies store user information and browsing habits. They can be classified as:
- Session Cookies: Temporary, deleted when the browser is closed.
- Persistent Cookies: Stored for a specified duration, even after closing the browser.
- First-Party Cookies: Set by the website for user experience and analytics.
- Third-Party Cookies: Set by external domains (e.g., advertisers) to track user behavior.
Cookies can breach security as they track personal info and preferences.
Password Security
Strong passwords protect accounts from unauthorized access. A good password should:
- Have a minimum of 10 characters
- Use both uppercase and lowercase letters
- Include at least one number
- Contain at least one special character
Encryption
Encryption protects data by converting it into a coded format.
Types of encryption include:
- Symmetric Encryption (Private Key Encryption)
- Uses one key for both encryption and decryption
- Example: AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
- Asymmetric Encryption (Public Key Encryption)
- Uses a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption
- Example: RSA
- Hashing (One-way Encryption)
- Converts data into a fixed-length string that cannot be reversed
- Example: SHA-256
Where Encryption is Used:
- Web Security: HTTPS (SSL/TLS encryption) protects websites from eavesdropping
- Messaging Apps: End-to-end encryption ensures messages stay private
Phishing Attacks
Phishing tricks users into revealing personal information through fake emails, messages, or websites.
Types of Phishing:
- Email Phishing: Fake emails pretending to be from trusted companies
- Website Spoofing: Fake websites that steal login credentials
- Smishing: Fake SMS messages from banks, delivery services, or government agencies
How to Stay Safe:
- Don’t click on links or download attachments from unexpected emails
- Check sender emails carefully for fake domains
- Type website URLs manually instead of clicking links
- Look for HTTPS and a padlock icon on websites
- Enable spam filters to block malicious messages
Verification
Verification ensures users, systems, and software are legitimate.
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
Added security requiring multiple independent authentication factors. -
Digital Signatures:
Cryptographic technique verifying the authenticity of digital documents. -
CAPTCHA:
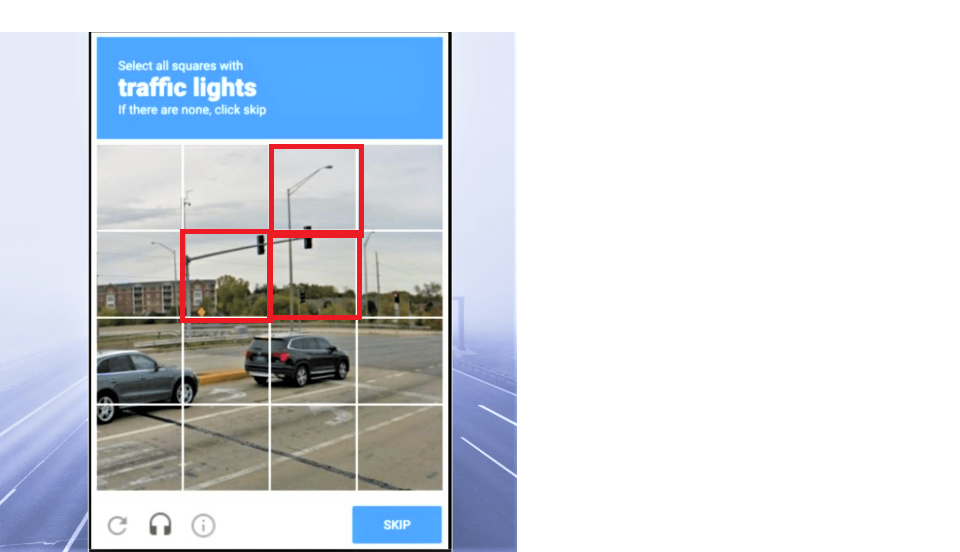
Ensures the user is human by asking them to complete simple tests (e.g. image selection).
🧠 Popcorn Hacks
🍪 Hack 1: Exploring Cookies
- Open Developer Tools (fn + F12 → Application → Cookies)
- Find a cookie from one site and analyze:
- Name
- Value
- Expiration Date
- Source (First-Party or Third-Party?)
Name: SSID Value: AqqkzWIO_x-WHBy3J Source: .youtube.com Expires: 2026-05-07T04:58:38.537Z —
🔐 Hack 2: Understanding CAPTCHA
🧩 Homework Hack: Play with Encryption
Random shift values:
import random
def caesar_cipher(text, shift, mode):
if shift == "random":
shift = random.randint(1, 25)
print(f"[INFO] Random shift used: {shift}")
result = ""
for char in text:
if char.isalpha():
shift_amount = shift if mode == "encrypt" else -shift
new_char = chr(((ord(char.lower()) - 97 + shift_amount) % 26) + 97)
result += new_char.upper() if char.isupper() else new_char
else:
result += char
return result
mode = input("Do you want to encrypt or decrypt? ").strip().lower()
message = input("Enter your message: ")
shift = input("Enter shift value (number or 'random'): ")
shift = int(shift) if shift.isdigit() else "random"
output = caesar_cipher(message, shift, mode)
print(f"Result: {output}")
[INFO] Random shift used: 6
Result: nkrru znoy oy g zkyz