The Digital Divide
Learn about the Digital Divide, and what we can do to reduce it. By Marti, Nikhil, & Aarav.
- Period 2: The Digital Divide
- Lesson Objective
- CSP Learning Objectives
- 🎬 Video: The Digital Divide in American High Schools
- 📉 Why Does the Divide Exist? (IOC-1.A, IOC-1.B)
- 🖥️ Why is Technology Access Important? (IOC-2.A)
- 🌉 Examples of Digital Infrastructure:
- ⚖️ Ethical and Societal Concerns (IOC-2.B)
- ✨ Solutions to Bridge the Divide
- As students, we can
- Popcorn Hacks
- Practice MCQs (AP CSP Style)
- A rural school district receives new funding to upgrade its internet infrastructure. Which of the following outcomes could most unintentionally widen the digital divide in that district?
- A national organization donates refurbished laptops to multiple low-income neighborhoods. Which scenario best illustrates a hidden challenge that can derail this well-intentioned effort?
- A city introduces an online public forum for local policy decisions to increase civic participation. Which action would best mitigate the risk of digital inequalities in this process?
- Homework Hack
Period 2: The Digital Divide
Lesson Objective
Students will:
- Define, analyze, and propose solutions to the digital divide globally, but specifically in our own community(SD)
- Contrast privileged and less privileged socioeconomic communities.
- Connect these disparities to broader CSP concepts, including:
- Computing innovations
- Ethics
- Societal impacts
CSP Learning Objectives
(Aligned with College Board)
IOC-1.A
Explain how computing innovations can reflect and amplify existing societal inequalities.
IOC-1.B
Explain how bias exists in computing innovations.
IOC-2.A
Describe the digital divide and its consequences on:
- Education
- Employment
- Healthcare
- Community participation
IOC-2.B
Identify and analyze ethical and societal concerns related to computing innovations.
🎬 Video: The Digital Divide in American High Schools
Takeaways (From the Video):
The digital divide significantly impacts students’ educational opportunities, particularly affecting those without reliable internet access. Addressing these disparities is crucial for ensuring equitable futures.
📉 Why Does the Divide Exist? (IOC-1.A, IOC-1.B)
- Economic Privilege: Wealthier areas can afford better infrastructure.
- Geographical Location: Rural or border communities often lack infrastructure investments.
- Societal Factors: Historical inequalities, language barriers, immigration status, and limited political representation.
Bias in Computing Innovations (IOC-1.B):
- Innovations typically favor wealthier users who can afford expensive technology.
- Algorithms and software often designed by privileged groups, unintentionally excluding diverse populations.
🖥️ Why is Technology Access Important? (IOC-2.A)
| Area | Importance of Digital Access | Consequences Without Access |
|---|---|---|
| Education 🎓 | Online learning, research, assignments | Lower academic performance, fewer opportunities |
| Employment 💼 | Job searching, remote work, skill training | Reduced career opportunities, lower income potential |
| Healthcare 🏥 | Telemedicine, health information, online appointments | Poorer health outcomes, limited medical services |
| Community Participation 🌎 | Civic engagement, social connection, community resources | Isolation, reduced civic voice |
🌉 Examples of Digital Infrastructure:
-
Strong Infrastructure: USA (urban), South Korea, Japan, Western Europe
-
Weak Infrastructure (Developing Nations): In many rural parts of Africa, India, and other developing regions, internet infrastructure is limited or nonexistent, causing entire communities to remain offline. While it’s easy to think about these locations as far away, the digital divide also affects areas that might seem more connected on the surface.
-
Weak Infrastructure (Rural USA - SD):
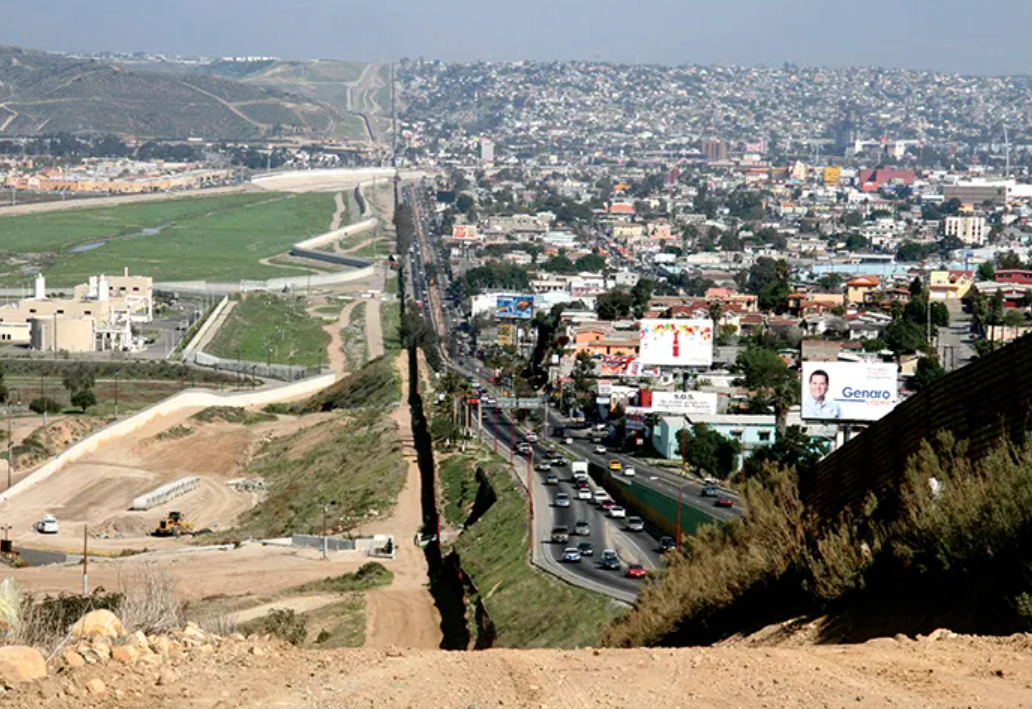

According to a 2023 article from The San Diego Union-Tribune, nearly 106,000 people in San Diego County alone lack adequate broadband access, impacting remote work, telehealth, and online education. This underscores that internet deserts can exist even in relatively affluent areas, demonstrating that the digital divide is not exclusively a distant or “developing world” challenge.
⚖️ Ethical and Societal Concerns (IOC-2.B)
🚪 Fairness
- Everyone deserves equal access to essential digital resources like the internet, computers, and digital tools.
- Limited access creates disadvantages in education, healthcare, and job opportunities.

✊ Social Justice
- Technology gaps reinforce existing inequalities, especially for marginalized communities.
- Lack of access to reliable internet and devices prevents individuals from competing equally in school and work.

🤝 Responsibility
- Bridging the digital divide requires shared effort from:
- 🏛️ Governments – Provide funding and infrastructure.
- 🏢 Corporations – Develop affordable technologies and expand access.
- 🏘️ Communities – Offer local resources like public Wi-Fi and computer access.

✨ Solutions to Bridge the Divide
🏙️ 1. Improve Infrastructure in Underserved Communities
- Expand internet access in rural and low-income areas.
- Install public Wi-Fi and community tech hubs.

💻 2. Subsidize Devices and Internet Costs
- Provide low-cost or free devices to students and low-income families.
- Offer government-funded internet programs.

🌍 3. Create Inclusive Technologies
- Design software and hardware that meet the needs of diverse communities.
- Ensure accessibility for individuals with disabilities.

📜 4. Public Policies Prioritizing Digital Equity
- Pass legislation supporting affordable internet access.
- Incentivize companies to expand network coverage.

As students, we can
- Teach peers – Offer tutoring on typing, internet use, and coding.
- Create guides – Make simple how-to guides for common tools.
- Collect devices – Run donation drives for laptops and tablets.
- Partner with businesses – Get sponsorships for new or used devices.
Popcorn Hacks
• Popcorn Hack 1: Identify one area (e.g., education, employment, healthcare, or community participation) where you’ve seen the digital divide in action. How does it affect people in different socioeconomic backgrounds?
• Popcorn Hack 2: Can you think of a computing innovation that might unintentionally exclude certain groups? Why might that happen?
Practice MCQs (AP CSP Style)
-
A rural school district receives new funding to upgrade its internet infrastructure. Which of the following outcomes could most unintentionally widen the digital divide in that district?
A. The new broadband network is never advertised, leaving only a few families aware of its availability.
B. The infrastructure upgrade is offered only at the main high school, leaving feeder schools with minimal connectivity.
C. The district requires a mandatory device insurance fee, which students in underserved areas may still struggle to pay.
D. Community organizations host digital literacy workshops in the evenings for families with limited scheduling flexibility.Show Answer
The correct answer is C. While limited locations or poor advertising can pose challenges, a mandatory insurance fee is most likely to perpetuate financial barriers for lower-income students, further widening the gap. -
A national organization donates refurbished laptops to multiple low-income neighborhoods. Which scenario best illustrates a hidden challenge that can derail this well-intentioned effort?
A. The donated laptops run older operating systems but fully support common productivity software.
B. The neighborhoods receive data-capped internet plans, making streaming and frequent updates cost-prohibitive.
C. The organization arranges part-time digital literacy instructors to teach basic computer skills.
D. Each laptop comes with built-in parental controls that require an additional subscription for advanced features.Show Answer
The correct answer is B. While older machines or parental controls may pose minor inconveniences, data caps severely limit usage, preventing true accessibility and further entrenching the digital divide. -
A city introduces an online public forum for local policy decisions to increase civic participation. Which action would best mitigate the risk of digital inequalities in this process?
A. The city mandates all participants to use encrypted messaging apps to ensure authenticity of input.
B. The city holds in-person “tech sessions” and subsidizes internet costs for underrepresented districts.
C. The forum only allows posting during non-business hours to ensure server reliability for all users.
D. The city partners with a private data analytics firm to filter out irrelevant comments.Show Answer
The correct answer is B. Offering both digital literacy training and subsidizing internet costs actively reduces barriers to participation, addressing core issues of the digital divide.
Homework Hack
Write 5 sentences describing what you have noticed about the digital divide in your own community. Consider how socioeconomic factors, location, and access to technology may play a role. Then explain how you can personally help bridge this gap—perhaps through awareness, advocating for policy changes, or supporting community-based tech programs. Make sure each sentence provides a clear insight or action step. Submit your 5 sentences in the next class.